Mount Rainier Volcanoes West Coast: A Comprehensive Guide
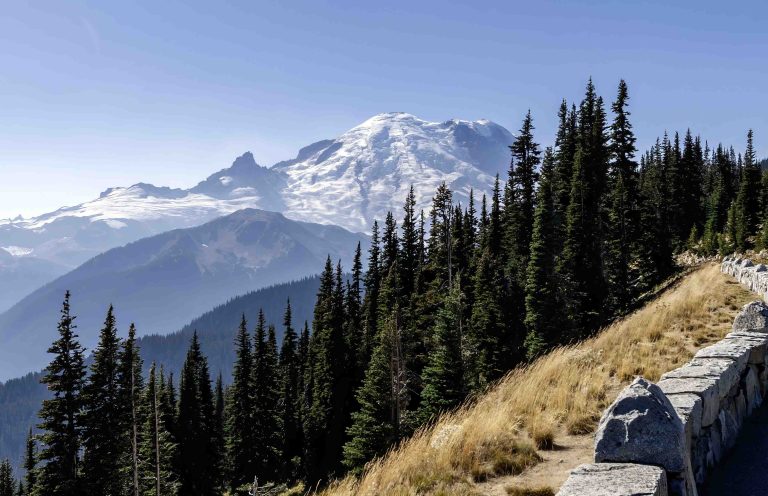
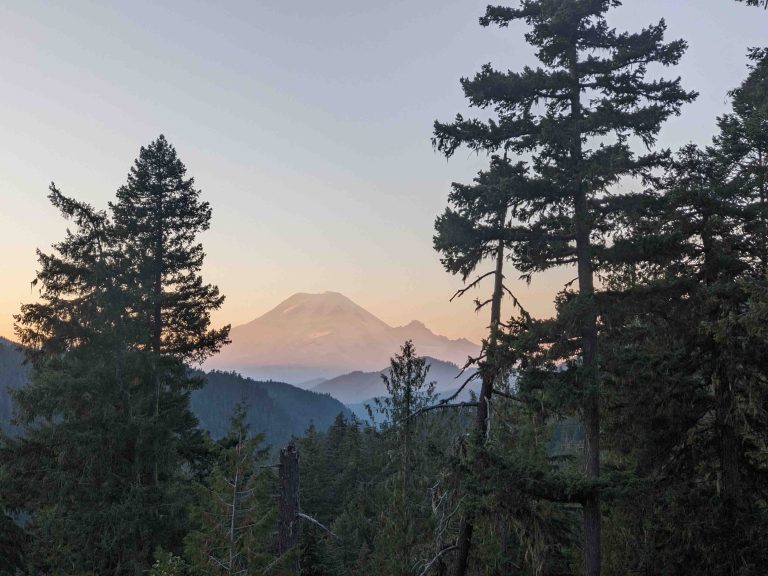
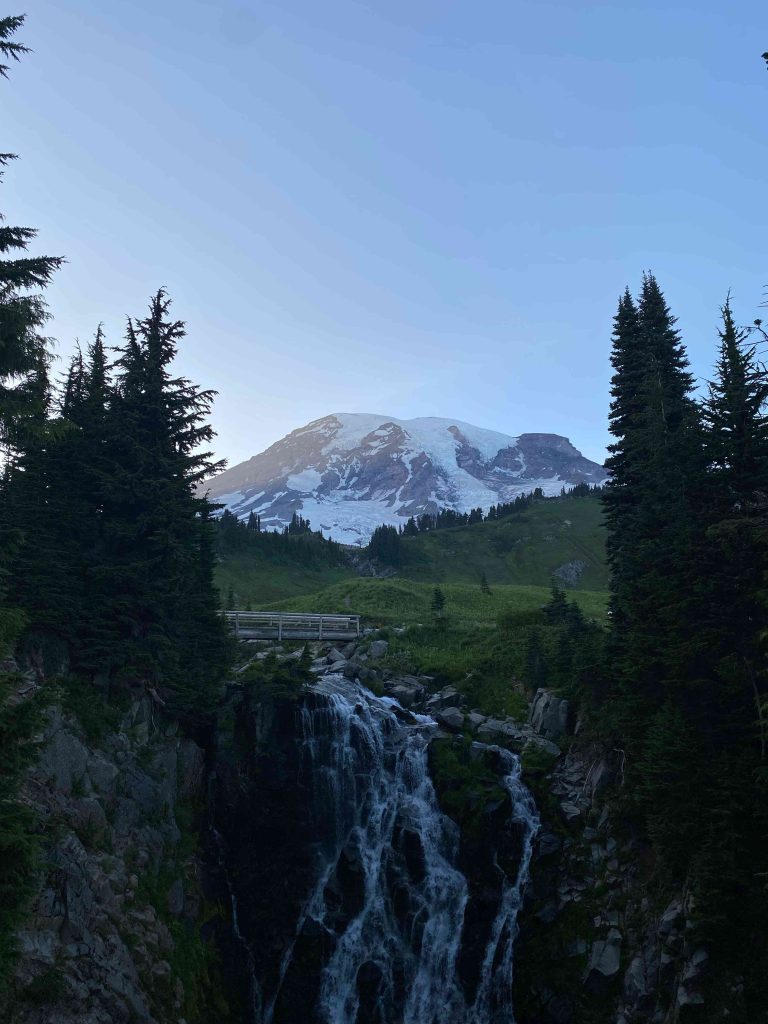
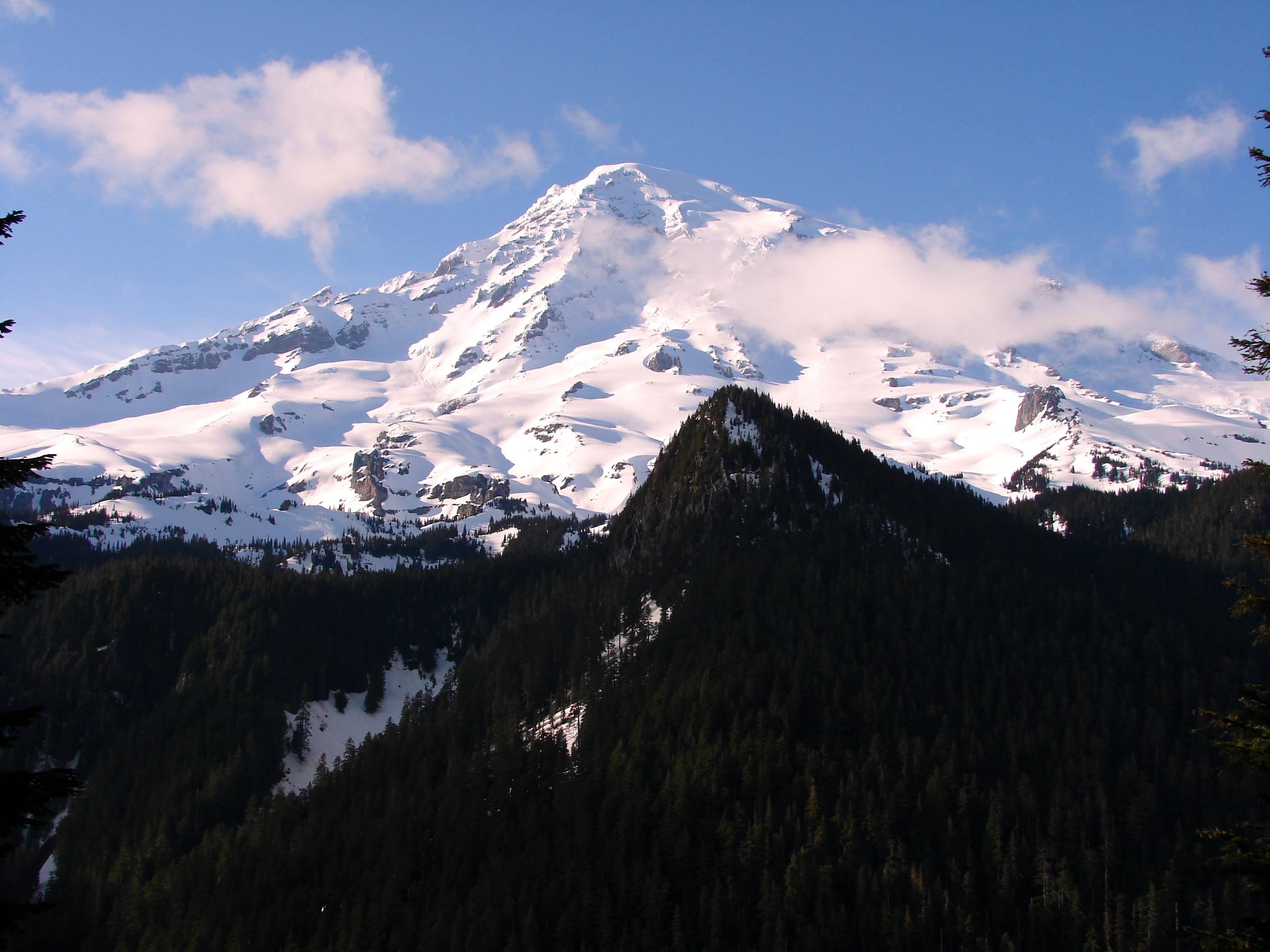
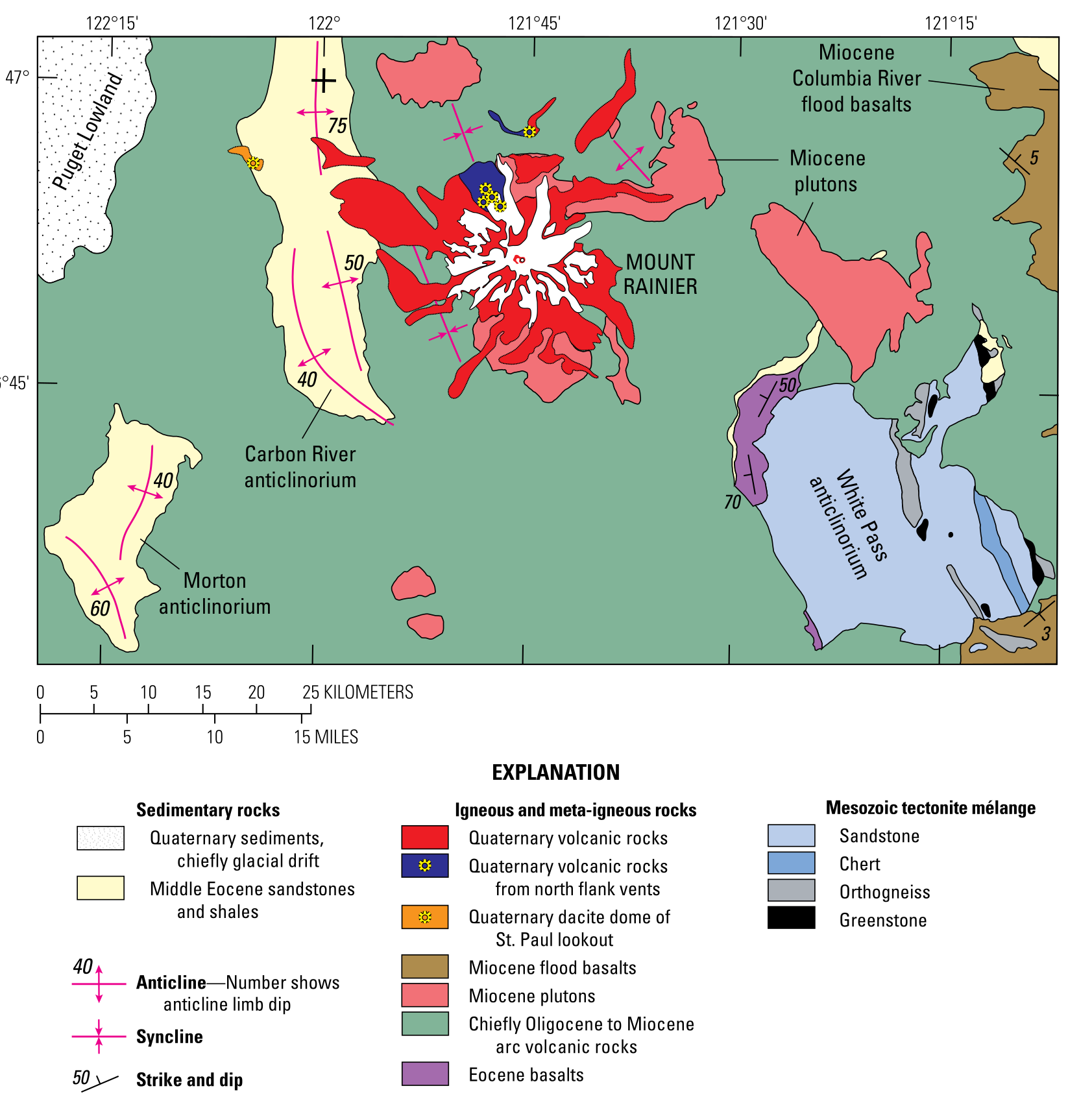
Mount Rainier, an iconic stratovolcano on the West Coast of the United States, stands as a testament to the region’s volcanic activity. As the most glaciated peak in the contiguous U.S., it dominates the Cascade Range landscape. This guide explores Mount Rainier’s geological history, recent eruptions, accessibility, and its significance among West Coast volcanoes. What … Read more