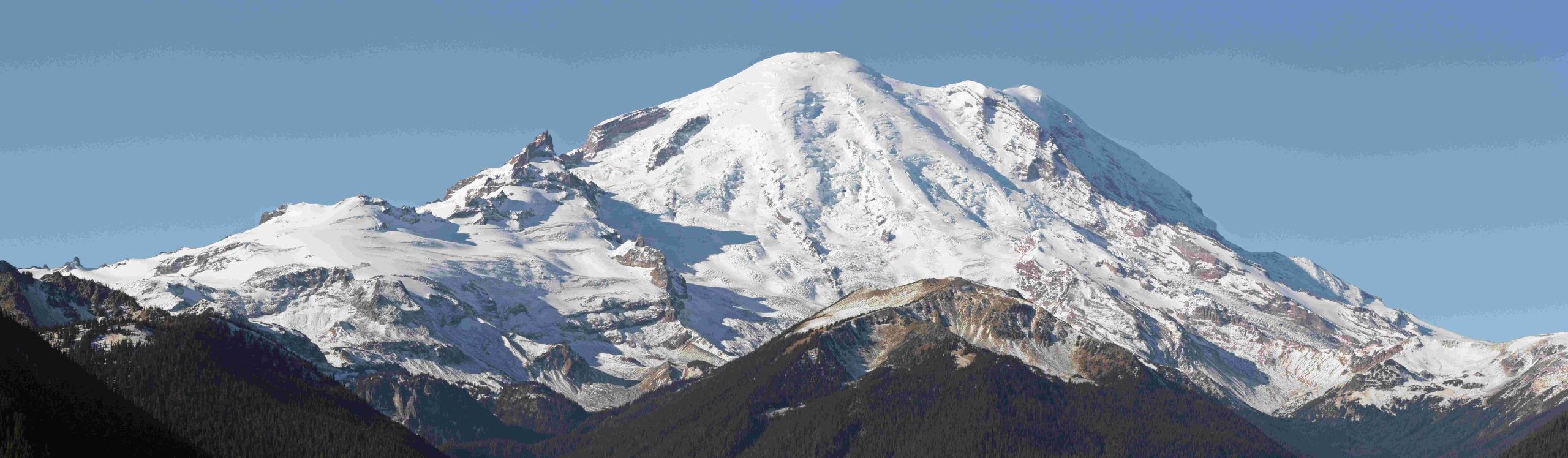
Mount Rainier, an iconic peak in Washington State, is renowned for its unique volcanic landscape, diverse ecosystems, and stunning wildflower meadows. As the tallest mountain in the Cascade Range and an active stratovolcano, Mount Rainier offers visitors a chance to explore glaciers, subalpine meadows, and dense forests. Its accessibility and range of visitor amenities make it a popular destination for nature enthusiasts, hikers, and photographers alike.
What Makes Mount Rainier’s Volcanic Landscape Unique?

Mount Rainier’s volcanic landscape is truly one-of-a-kind, featuring several distinctive geological and volcanic elements:
- Impressive Elevation: Standing at 14,410 feet (4,392 meters), Mount Rainier is the highest peak in the Cascade Range and the fourth highest mountain in the contiguous United States.
- Extensive Glacial System: The mountain boasts the largest glacial system in the lower 48 states, with at least 25 named glaciers. These include:
- Carbon Glacier
- Cowlitz-Ingraham Glacier
- Emmons Glacier
- Kautz Glacier
- Nisqually Glacier
- Paradise-Stevens Glacier
- Winthrop Glacier
These glaciers not only shape the landscape but also serve as crucial indicators of climate conditions.
- Volcanic Activity: Although currently dormant, Mount Rainier is an active volcano. Its landscape has been sculpted by past lava flows and eruptions. Seismic activity is continuously monitored to track potential volcanic activity.
- Diverse Geologic Formations: The mountain’s geology is complex, featuring various landforms and watersheds shaped by both volcanic and glacial activities. The road from White River to Sunrise offers visitors a journey through Mount Rainier’s geologic history, showcasing its diverse formations.
How Diverse Are Mount Rainier’s Ecosystems?

Mount Rainier National Park encompasses a wide range of ecosystems, supporting a rich variety of flora and fauna:
- Elevation Zones:
- Lowland forests (lower elevations)
- Subalpine meadows (around 4,500 feet)
-
Alpine meadows (above timberline, approximately 7,000 feet)
-
Flora:
- Lower elevations: Dense coniferous forests with giant Douglas firs, western red cedars, and mountain hemlocks
- Higher elevations: Various fir species and western white pines
-
Subalpine and alpine meadows: Renowned for colorful wildflower displays
-
Fauna:
- Over 65 mammal species, including:
- Black-tailed deer
- Roosevelt elk
- Black bears
- Mountain goats
- More than 220 bird species, such as:
- Gray jays
- Steller’s jays
- Clark’s nutcrackers
- Hairy woodpeckers
- 14 amphibian species
- 5 reptile species
- 14 native fish species
The park’s varied habitats and life zones contribute to its exceptional biodiversity, making it a haven for wildlife enthusiasts and researchers alike.
What Makes Mount Rainier’s Wildflower Meadows So Stunning?
Mount Rainier’s wildflower meadows are a major attraction, drawing visitors from around the world:
- Peak Bloom Times: Mid-July to early August (varies depending on weather conditions)
- Popular Wildflower Species:
- Lupine
- Avalanche lily
- Various alpine flowers
| Location | Features |
|---|---|
| Paradise | Spectacular subalpine meadows |
| Sunrise | High-elevation wildflower displays |
| Wonderland Trail | Diverse wildflower viewing along the trail |
While specific guided tours focused solely on wildflowers may not be available, the park’s visitor centers and ranger programs often provide information and guided hikes that include wildflower viewing. Visitors can check the park’s website or inquire at visitor centers for the best times and locations to see the wildflowers in bloom.
What Visitor Amenities and Accessibility Options Does Mount Rainier Offer?
Mount Rainier National Park provides various amenities and accessibility options for visitors:
- Parking Facilities:
- Paradise Visitor Center
- Sunrise area
-
Popular trailheads throughout the park
-
Visitor Centers:
- Paradise Visitor Center
- Sunrise Visitor Center
- Ohanapecosh Visitor Center
These centers offer information on trails, wildlife, and park activities.
- Trail Accessibility:
- Over 260 miles of maintained trails
- Range from easy day hikes to challenging multi-day treks (e.g., Wonderland Trail)
-
Many trails accessible by car, with paved road access points on eastern and southern sides of the park
-
Transportation Options:
- Personal vehicle (most common)
- No direct public transportation to the park
-
Shuttle services and tour operators available from nearby cities like Tacoma or Seattle
-
Challenges and Costs:
- Unpredictable weather, with significant snowfall in winter
- Potential for snow at higher elevations year-round
- Trail difficulty varies widely
- Entrance fees required for park access
- Additional fees for some activities (e.g., Mt. Rainier Gondola at Crystal Mountain Resort)
Mount Rainier’s unique combination of geological features, diverse ecosystems, stunning wildflower meadows, and accessible visitor amenities make it a truly special destination for nature lovers and outdoor enthusiasts.
References:
- https://visitrainier.com/mt-rainier-fact-sheet/
- https://morethanjustparks.com/mount-rainier-facts/
- https://www.britannica.com/place/Mount-Rainier-National-Park